Reveal the Transformative Power of Concrete Scanning in Making The Most Of Effectiveness and Safety And Security
Concrete scanning has actually emerged as a crucial device in the building sector, offering unmatched benefits in boosting task effectiveness and making certain safety criteria. The transformative power of concrete scanning lies in its capacity to give real-time data and thorough insights, revolutionizing just how projects are intended and implemented.
Relevance of Concrete Scanning
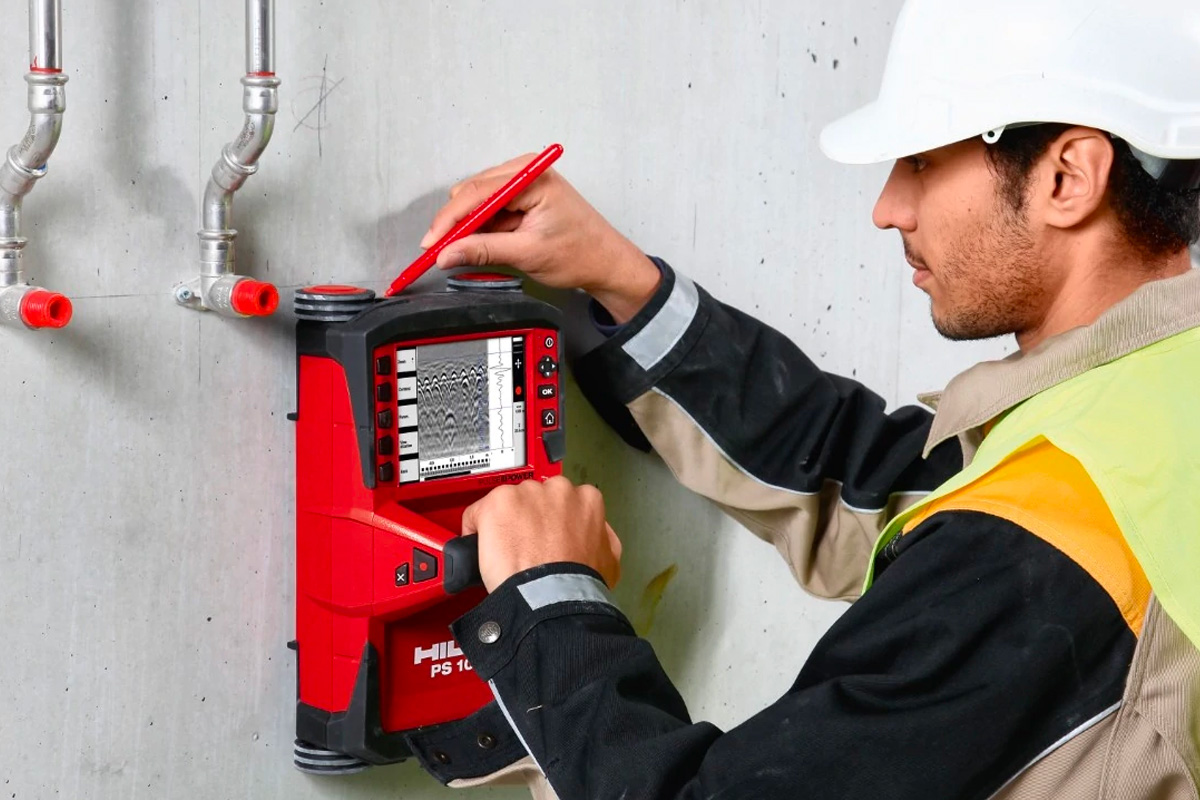
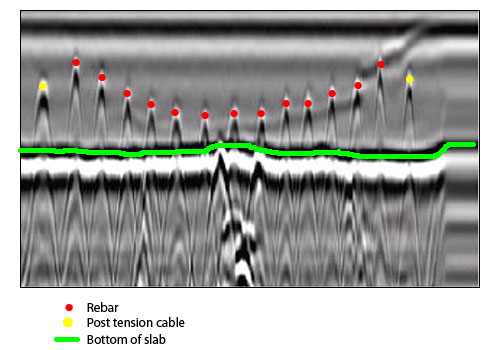
Guaranteeing the structural integrity and security of building projects starts with the important action of performing comprehensive concrete scanning. Concrete scanning is a non-destructive method made use of to find and map subsurface components within concrete structures. This procedure is crucial in recognizing possible risks, such as rebar, post-tension cables, and conduits, that might be concealed within the concrete. By making use of advanced modern technologies like ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electro-magnetic induction, construction groups can precisely locate these elements without triggering any kind of damages to the framework.
The importance of concrete scanning can not be overstated, as it plays a vital function in stopping mishaps, reducing task delays, and ensuring the long-lasting resilience of the building. By determining possible dangers prior to the building phase begins, contractors can carry out appropriate precaution and make educated choices concerning the layout and execution of the task. Furthermore, concrete scanning helps in optimizing project timelines and budget plan by staying clear of unexpected expenses and delays that may arise as a result of unforeseen blockages within the concrete. Inevitably, purchasing extensive concrete scanning is an aggressive method that boosts both effectiveness and safety in building and construction tasks.
Just How Concrete Scanning Works
Concrete scanning operates as a crucial device in construction jobs by employing innovative technologies to find and map subsurface components without creating structural damages. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) are 2 primary approaches used in concrete scanning.
During the scanning procedure, the data collected is analyzed in real-time, permitting immediate identification of prospective hazards or obstacles beneath the surface area. This details help in decision-making, making certain that building and construction activities proceed safely and efficiently. In addition, 3D imaging software application can be used to develop topographic maps of the subsurface elements, additionally improving task preparation and implementation. By utilizing these advanced technologies, concrete scanning substantially minimizes the threat of pricey damages and injuries on construction sites.
Advantages of Concrete Scanning
Using advanced scanning modern technologies in building tasks offers a wide variety of benefits, improving both efficiency and safety on-site. Among the key advantages of concrete scanning is the capability to spot and situate ingrained things such as rebar, post-tension wires, and avenues precisely. By recognizing these components prior to exploration or reducing right into concrete structures, the danger of accidental strikes is dramatically decreased, stopping possible injuries to employees and damages to the framework itself. Concrete scanning helps in preparation and creating more successfully, as it supplies exact info concerning the location and depth of structural elements.

Study: Concrete Scanning Success
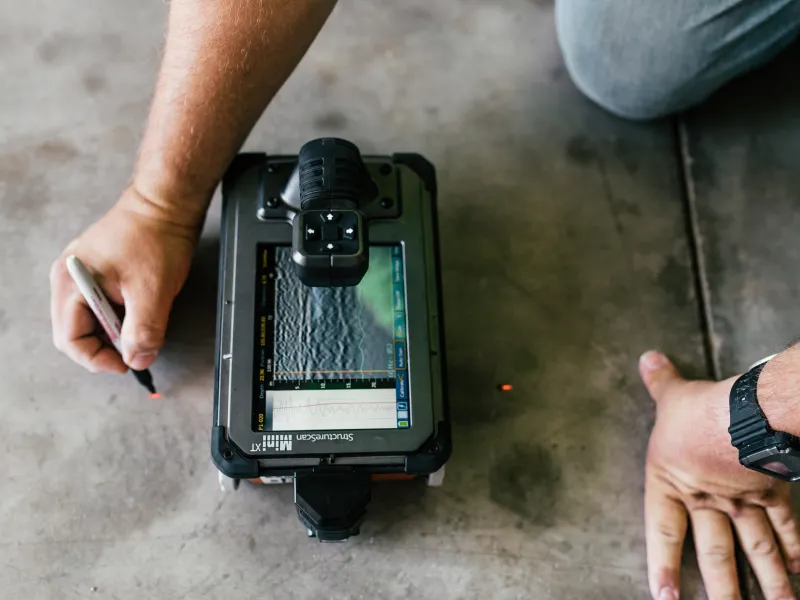

In one more situation, a building business made use of 3D concrete scanning to examine the condition of aging concrete frameworks in a historic structure. The detailed scans offered useful understandings into the degree of damage and helped prioritize upkeep initiatives efficiently. By proactively resolving areas of problem determined via scanning, the firm was able to prolong the lifespan of the framework and make sure owner safety and security.
These instance research studies highlight the transformative power of concrete scanning in enhancing performance, precision, and safety in building and construction tasks.
Executing Concrete Scanning in Projects
Executing sophisticated scanning technologies throughout building and construction projects has become increasingly vital for enhancing accuracy and security. By incorporating concrete scanning into job planning and execution, construction teams can determine potential hazards, such as rebar or post-tension cords, concealed within concrete structures. This proactive technique minimizes the danger of mishaps, delays, and expensive rework, ultimately resulting in much more reliable project timelines index and budget plans.
To execute concrete scanning successfully, task managers ought to collaborate closely with knowledgeable scanning specialists to determine the most ideal scanning methods for the specific job demands. Involving scanning professionals from the onset of a project makes it possible for the team to create extensive scanning strategies that address essential locations of worry and ensure thorough information collection.
Moreover, including concrete scanning into routine task workflows can enhance decision-making processes, as real-time check data supplies instant insights right into the problem of concrete frameworks - Concrete Scanning. This data-driven approach promotes notified analytical and enables groups to make adjustments quickly, promoting a culture of effectiveness and security throughout the task lifecycle
Conclusion
To conclude, concrete scanning plays an essential function in enhancing efficiency and security in building projects. By using advanced modern technology to map and find out underlying structures within concrete, this process helps to stop costly blunders, make certain architectural honesty, and lessen threats on site. With the capacity to uncover concealed elements and supply accurate data, concrete scanning proves to be an important tool for maximizing project outcomes and making best use of overall success.
Concrete scanning is a non-destructive method used to identify and map subsurface elements within concrete structures. Furthermore, concrete scanning aids in maximizing project timelines and spending plan by avoiding unexpected expenses and delays that may occur due to unpredicted obstructions within the concrete. One significant situation research includes a massive renovation job where concrete scanning played a critical function in guaranteeing task success.In another situation, a building business used 3D concrete scanning to assess the problem of maturing concrete frameworks in a historical structure. By integrating concrete scanning right into job planning and implementation, building and construction teams can recognize possible dangers, such as rebar or post-tension cables, hidden within concrete frameworks.